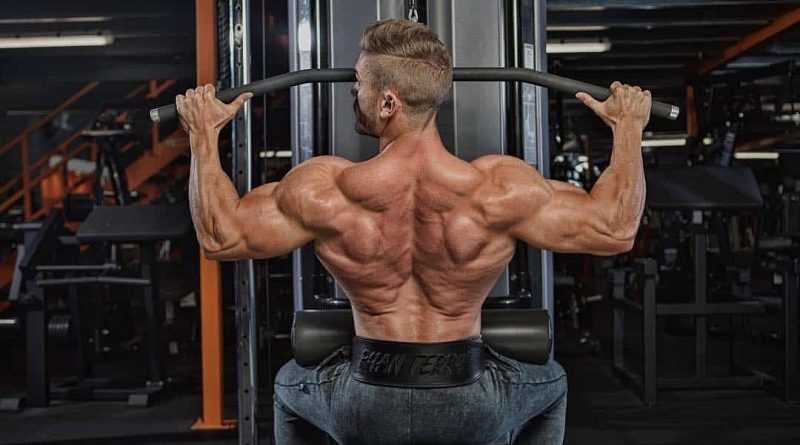
Lat Pull-Down
How to do Lat Pull-Down, which is a basic movement among back and wing exercises? What muscles does Lat Pull-Down work? What are the benefits of Lat Pull-Down? You will find the most detailed information about the Pull-Down movement in this
| Name | Lat Pull-Down |
| Exercise Type | Strength |
| Skill Level | Beginner |
| Equipment Needed | Pull Machine |
| Muscles Worked | Primary: Latissimus Dorsi |
| Mechanics | Compound |
| Force | Pull |
| Alternative Forms/Substitute | Pull-up |
Lat Pull-Down
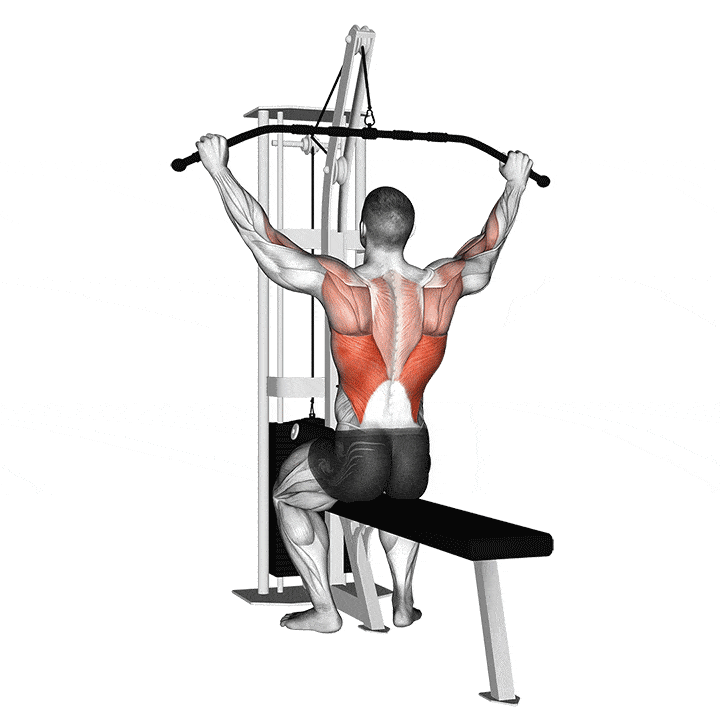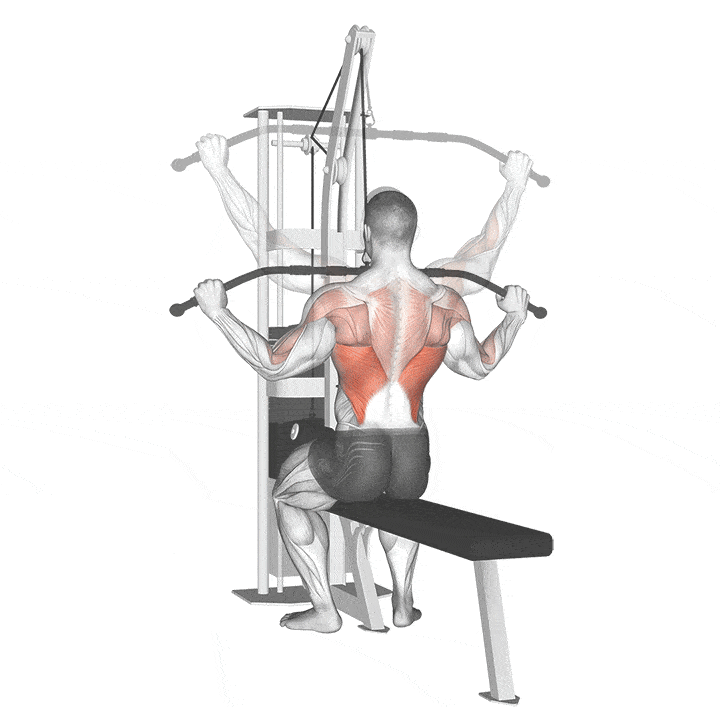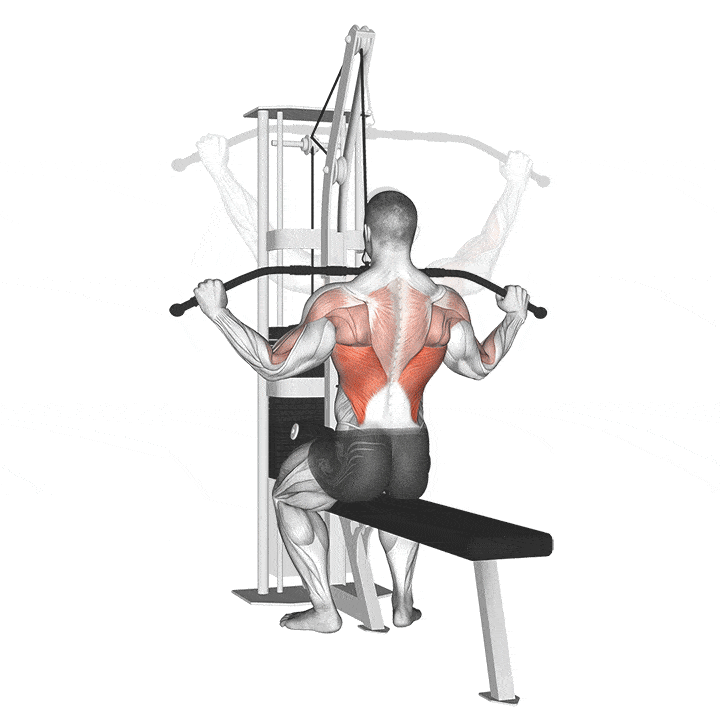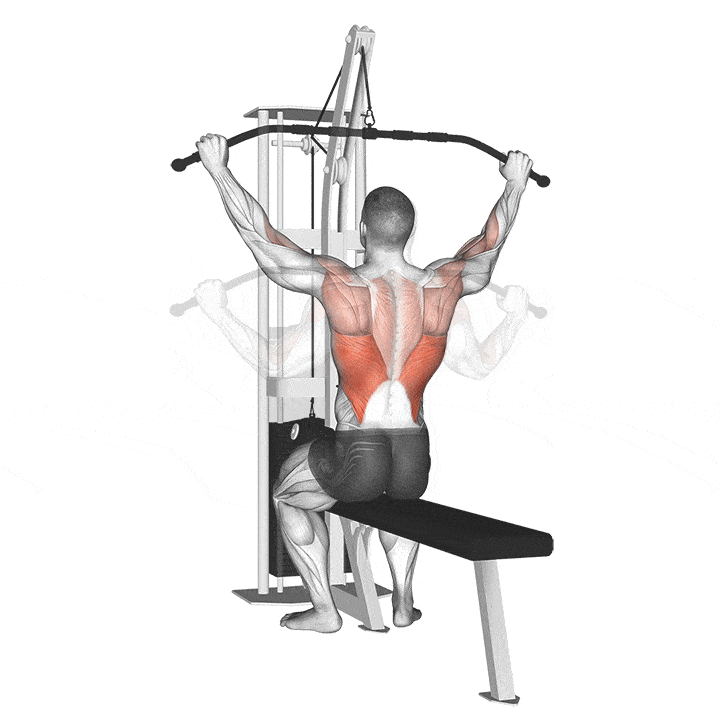
How to do Lat Pull-Down
Lat pull down effectively targets large back muscles, but should be done without burdening the shoulder or waist. Follow the directions given to reduce the stress applied to these two areas.
- Sit on the coffee table with your back straight.
- Open your arms wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Exhale as you slowly pull the iron bar towards your upper chest.
- As you slowly return the iron bar to its starting position, breathe.
- Repeat for the number of sets.
Lat Pull Down Grip Positions
There is confusion that a wide grip pull down activates the latissimus dorsi and other muscles more than a narrow grip. Andersen et al. (2014) conducted a research study to examine this question. 15 men participated in the study. Using electromyographic (EMG) activity, the researchers compared three different pronate grip widths: near, medium, and wide grips (1, 1.5, and 2 times biachromial distance).
They found that during the concentric phase of the exercise, the latissumis dorsi worked similarly between the three grips. However, the biceps brachii tended to have higher activation levels using a narrow or medium grip rather than a wide grip. The wide and medium grip showed more activation of the latissimus dorsi than the narrow grip during the eccentric phase of the exercise. For this reason, the researchers suggest that a wide to medium grip might be a slightly better option, but sports enthusiasts and athletes give similar results in strength and muscle size, no matter which grip they choose.

What muscles does Lat Pull-Down Work?
The muscles that are active in the first phase of the movement are the teres major, the upper part of the pectoralis major, the biceps brachii, the infraspinatus, and the latissimus dorsi. In the later phase of movement, the latissimus dorsi, infraspinatus, and teres major are the main muscles that are active.(1)
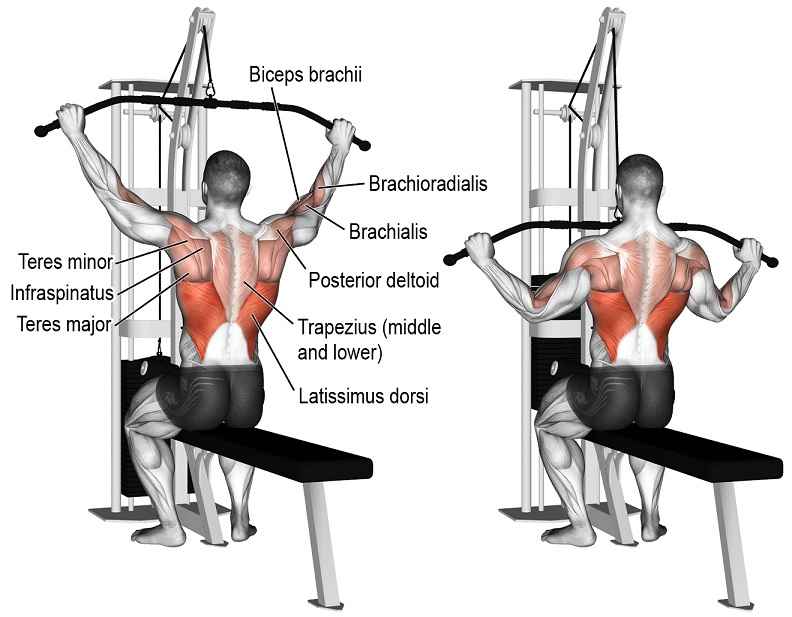
Target
Latissimus Dorsi
Synergists
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Biceps Brachii
- Teres Major
- Infraspinatus
- Posterior Deltoid
- Rhomboids
- Levator Scapulae
- Teres Minor
- Trapezius, Lower and Middle
- Pectoralis Major
Dynamic Stabilizers
Triceps, Long Head
What are the Benefits of Lat Pull-Down?
Looking at the computer and phone all day can cause hunchback and pain. It can also cause strain in your back and shoulders due to inadequate use of other nearby muscles. However, regular muscle strengthening exercise will help strengthen these muscles, potentially improving your posture, reducing pain, and improving the overall health of your muscle tissue.
- It allows you to make a stronger upper body. Among the movements to develop the back muscles, the most effective area of pull-down movement is the development of the Latissimus dorsi, that is, the superficial back muscles. Exercises such as Lat pull down and Pull-up are very successful for body strength.
- Infraspinatus and Scapula affect the muscles covering the scapula, preventing problems caused by muscle weakness such as postural posture and shoulder blade protrusion. Seems very useful..
- The most common problem in shoulder injuries is weak cuff muscles. It provides interaction in Teres minor and teres major muscle groups for the development of the rear shoulder and wing muscles. In this way, you can create a stronger back wing and shoulder structure. The development of these muscles makes the shoulders more resistant to injury.
- Lat pull-down exercise, in a study, it was observed that a patient with spinal cord injury (SCI) had positive effects on lower extremity muscle strength and spine shape. (2)
- The latissimus dorsi. It’s the broadest muscle group of the back and is responsible for the highly sought-after “V-taper.” A wide back is essential when building a V-taper. There are two different ways to develop well developed lats and an impressive back. One of the approaches is to do pull-down movements and pull-up movements, the other is to do rowing movements and deadlifts. Drop-down exercises create width and rowing movements create thickness. You can’t have an impressive back without the combination of the two.
Lat Pulldown vs Pull-up
The target of both pull-up and lat pulldown exercises is the back muscles. However, there is a big difference between the two. While latitude reduction is an open chain exercise, pulling up is a closed chain exercise. Studies indicate that closed-chain exercises may result in higher motor unit intake (activation of more muscle fibers) compared to open-chain exercises (Augustsson et al., 1998; Brindle et al., 2002; Uçar et al., 2014). In addition, in a study by Doma, Deakin, and Ness (2013), it was concluded that the chin-up movement is a more “functional” exercise compared to the latitude angle.
Lat Pull-Down vs Neck Pull-Down
Neck pull-down is a bit controversial and should be avoided. A pull-down on the back of the neck can cause more stress on the ligaments and shoulder capsule. Some researchers think that this exercise movement may pose a risk to cuff muscles. This may be due to its excessive external rotation while exercising, but more research is needed to support or refute this claim.
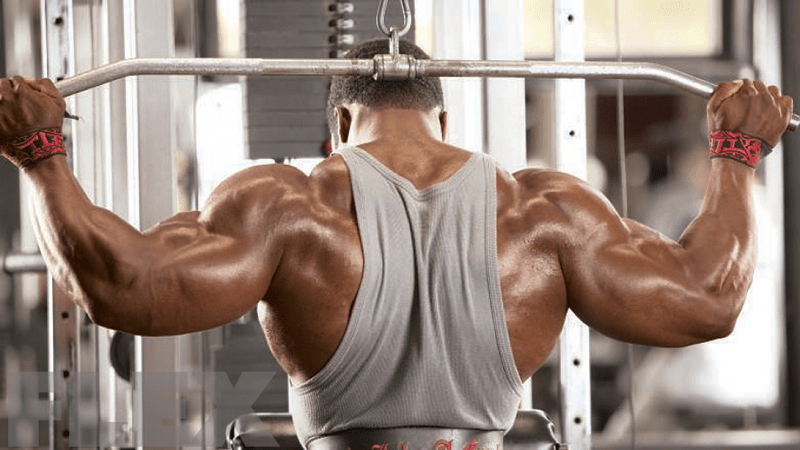

In studies (Yip, Chiu, & Poon, 2008; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas et al., 2007) a forward head posture has also been noted in neck injury and even headache. Therefore, individuals should aim to do resistance training exercises with a neutral cervical spine posture.
Back-to-neck pulls require the individual to extend the head forward so that the bar provides a clear path towards the base of the neck. A forward head posture can increase the muscle tension of several major neck muscles.
The two basic studies comparing placing the bar to the back or the front found no difference either in terms of latissimus study between these two positions. Overall, the results supporting the pull down position were more positive. Therefore, the rear pull does not have any advantage in terms of effective bodybuilding.
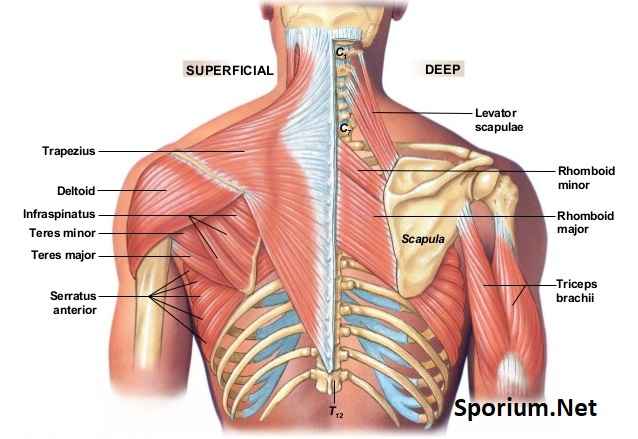
Back and Wing Muscles Anatomy
- Trapezius
- Latissimus dorsi
- Rhomboideus major
- Rhomboideus minor
- Levator scapula
- Serratus posterior superior
- Serratus posterior inferior
- Splenius capitis
- Splenius cervicis